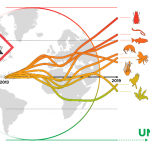
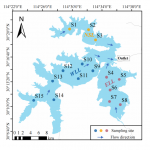
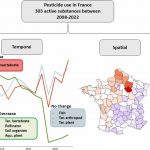
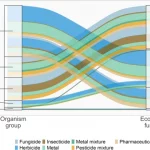
In this post, Jakob Wolfram and Ralf Schulz talk about their recent study published in Science, uncovering that the total applied toxicity of pesticides is rising, thus threatening the UN Biodiversity goal (COP15) of reducing pesticide risks globally by 50%.
Continue readingPesticide Toxicity is Rising — And It’s Putting the UN’s 2030 Biodiversity Goal at Risk